目录
- 1 冒泡排序(Bubble Sort)
- 2 选择排序(Selection Sort)
- 3 插入排序(Insertion Sort)
- 4 堆排序(Heap Sort)
- 5 归并排序(Merge Sort)
- 6 快速排序(Quick Sort)
- 7 Shell排序(Shell Sort)
1 冒泡排序(Bubble Sort)
算法描述
- 假设要从小到大进行排序
- 对于一个元素可比较的序列,从始元素开始,依次比较与之相邻的元素,如果大于后者,则二者位置互换
- 第一次遍历整个序列,最大的元素一定会移动到序列尾
- 第二次遍历整个序列(不包括序列尾元素),倒数第二大的元素会移动到序列倒数第二的位置
- .
- 遍历n-1次之后,整个序列排序完毕
算法动画演示
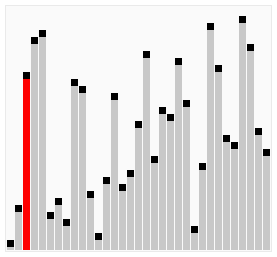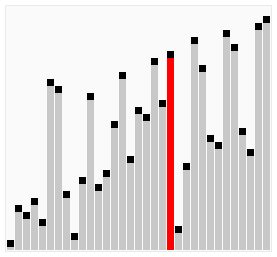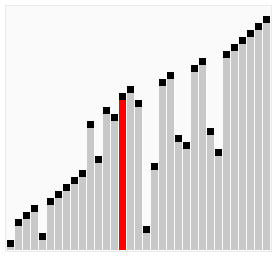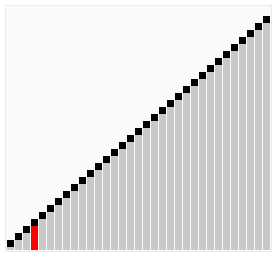
算法实现(Java)
import java.util.Random ;
public class BubbleSort{
/*
* This algorithm is not optimal, because we compare the element which has already ordered
* when the sequence is ordered, it terminate. We know this from the boolean sorted
*/
static void bubbleSort(int[] array){
boolean sorted = false ;
while(sorted = !sorted){
for(int i=0; i<array.length-1; i++){
if(array[i] > array[i+1]){
swap(array, i, i+1) ;
sorted = false ;
}
}
}
}
/*
* This algorithm for bubble sort is optimal, because we will not compare the element which has already ordered
* The abrove method also can be revised by assign a new variable hi=array.length then hi --
*/
static void bubbleSortRevised(int[] array, int lo, int hi){
boolean sored = false ;
while(sorted = !sorted){
for(int i=lo; i<hi-1; i++){
if(array[i] > array[i+1]){
swap(array, i, i+1) ;
sorted = false ;
}
}
hi -- ;
}
}
/*
* This is the revised version for method bubbleSort()
*/
static void bubbleSort2(int[] array){
boolean sorted = false ;
int hi = array.length ;
while(sorted = !sorted){
for(int i=0; i<hi-1; i++){
if(array[i] > array[i+1]){
swap(array, i, i+1) ;
sorted = false ;
}
}
hi -- ;
}
}
static void swap(int[] array, int first, int last){
int temp = array[first] ;
array[first] = array[last] ;
array[last] = temp ;
}
public static void main(String args[]){
Random rnd = new Random(26) ;
int[] array = new int[10] ;
for(int i=0; i<array.length; i++){
array[i] = rnd.nextInt(10) ;
}
bubbleSort(array) ;
//bubbleSortRevised(array, 0, array.length) ;
for(int i : array)
System.out.print(i + "\t") ;
}
}
复杂度分析
The best average worse case for bubble sort is in O(n^2)
2 选择排序(Selection Sort)
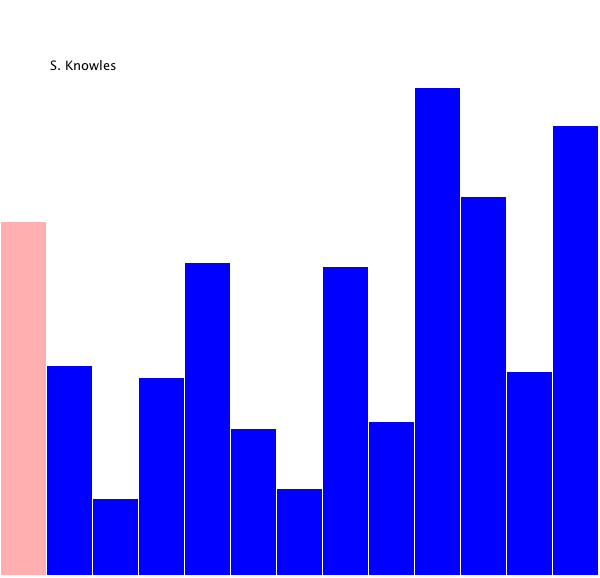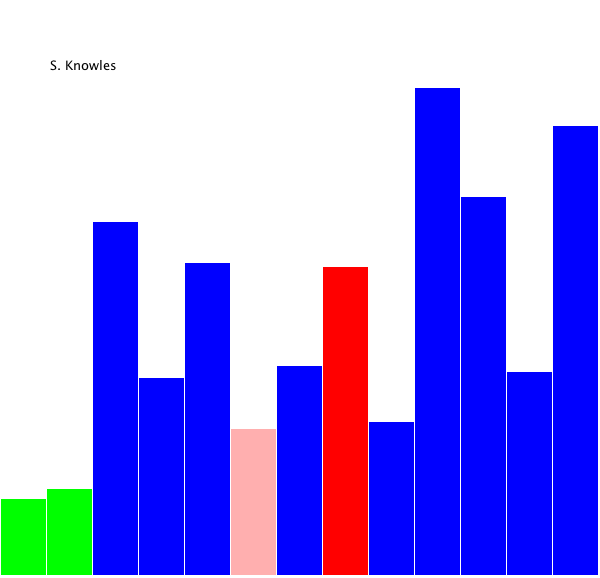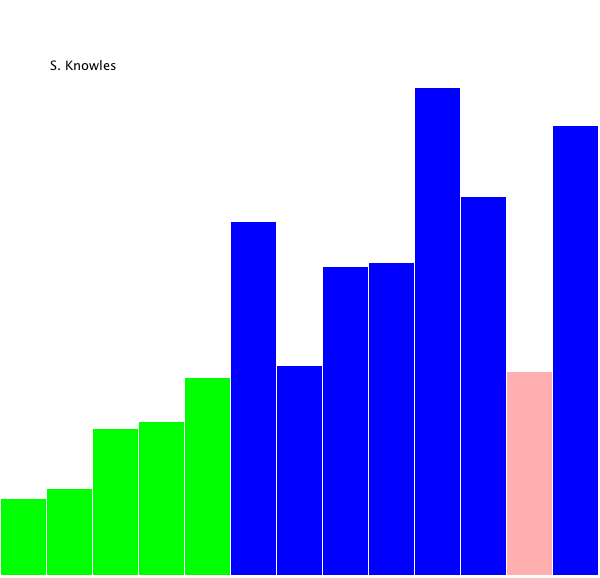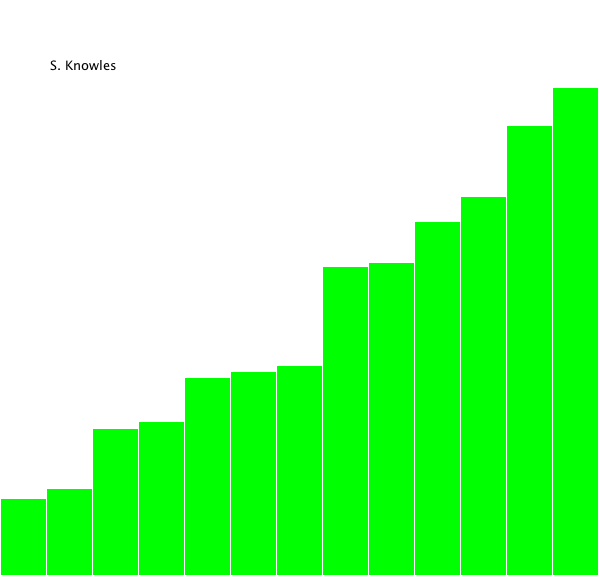
算法描述
- 共要进行n-1次selection遍历
- 每次遍历选择最小的元素,和起始遍历位置的元素进行互换
- 每一次遍历后最小的元素就位于进行起始遍历的位置
算法动画演示
算法实现
import java.util.Random ;
import org.fmz.container.Vector ;
import org.fmz.container.FixedVector ;
public class SelectionSort{
static void selectionSort(Vector vec){
int current ; // point to which selection processing(we need process n-1 times)
int pos ; // in each selection iteation, point to which element we will compare
int small_pos ; // in each selection iteration, store the smallest element position
Comparable smallest ; // in each selection iteration, store the smallest element
int n = vec.size() ;
for(current=0; current<n-1; current++){
small_pos = current ;
smallest = (Comparable)vec.elementAt(small_pos) ;
for(pos=current+1; pos<n; pos++){
if(((Comparable)vec.elementAt(pos)).compareTo(smallest) < 0){
small_pos = pos ;
smallest = (Comparable)vec.elementAt(pos) ;
}
}
if(small_pos != current)
swap(vec, current, small_pos) ;
}
}
static void swap(Vector vec, int first, int last){
Object temp = vec.elementAt(first) ;
vec.replace(first, vec.elementAt(last)) ;
vec.replace(last, temp) ;
}
public static void main(String args[]){
Random rnd = new Random() ;
FixedVector fvec = new FixedVector() ;
fvec.append(rnd.nextInt(10)) ;
fvec.append(rnd.nextInt(10)) ;
fvec.append(rnd.nextInt(10)) ;
fvec.append(rnd.nextInt(10)) ;
fvec.append(rnd.nextInt(10)) ;
fvec.append(rnd.nextInt(10)) ;
fvec.append(rnd.nextInt(10)) ;
fvec.append(rnd.nextInt(10)) ;
fvec.append(rnd.nextInt(10)) ;
fvec.append(rnd.nextInt(10)) ;
selectionSort(fvec) ;
for(int i=0; i<fvec.size(); i++)
System.out.print(fvec.elementAt(i) + "\t") ;
}
}
复杂度分析
The best average worst case for SelectionSort is in O(n^2)
3 插入排序(Insertion Sort)
算法描述
- 插入排序就像是玩扑克牌一样,我们将新得到的牌与手中的牌(手中的牌已经排好序)对比
- 找到与得到的牌相比小的牌,即插入这张小牌的后面
- 后面的牌次序依次后移
- 经过n-1此之后手中的牌就排好序了
算法动画演示
算法实现
import java.util.* ;
import org.fmz.container.Vector ;
import org.fmz.container.FixedVector ;
public class InsertionSort{
static void insertionSort(Vector vec){
int current ;
int pos ;
int n = vec.size() ;
for(current=1; current<n; current++){
pos = current ;
while(pos>0 && ((Comparable)vec.elementAt(current)).compareTo(vec.elementAt(pos-1)) < 0)
pos -- ;
if(pos != current){
vec.insertAt(pos, vec.elementAt(current)) ;
vec.removeAt(current+1) ;
}
}
}
public static void insertionSort_v2(int[] array, int lo, int hi){
int current ;
int pos ;
int insert_value ;
for(current = lo + 1; current < hi; current ++){
pos = current - 1 ;
insert_value = array[current] ;
while(pos >= lo && insert_value < array[pos]){
array[pos + 1] = array[pos] ;
pos -- ;
}
array[pos + 1] = insert_value ;
}
}
public static void main(String args[]){
Random rnd = new Random() ;
/*
FixedVector fvec = new FixedVector() ;
fvec.append(rnd.nextInt(10)) ;
fvec.append(rnd.nextInt(10)) ;
fvec.append(rnd.nextInt(10)) ;
fvec.append(rnd.nextInt(10)) ;
fvec.append(rnd.nextInt(10)) ;
fvec.append(rnd.nextInt(10)) ;
fvec.append(rnd.nextInt(10)) ;
fvec.append(rnd.nextInt(10)) ;
fvec.append(rnd.nextInt(10)) ;
fvec.append(rnd.nextInt(10)) ;
*/
int[] array = new int[10] ;
for(int i = 0; i<array.length; i++)
array[i] = rnd.nextInt(10) ;
//insertionSort(fvec) ;
insertionSort_v2(array, 0, array.length) ;
for(int i : array)
System.out.print(i + "\t") ;
}
}
复杂度分析
average case for Insertion Sort in O(n^2)
4 堆排序(Heap Sort)
算法描述
- 需要构建一个Heap数据结构
- 将序列添加到MaxHeap中
- 依次删除MaxHeap的root元素,即为剩余元素中的最大元素
算法动画演示

算法实现
import java.util.Random ;
import org.fmz.container.Vector ;
import org.fmz.container.FixedVector ;
import org.fmz.container.MaxHeap ;
public class HeapSort{
static void heapSort(Vector vec){
MaxHeap temp = new MaxHeap(vec.size()) ;
for(int i=0; i<vec.size(); i++)
temp.insert((Comparable)vec.elementAt(i)) ;
for(int i=vec.size()-1; i>=0; i--)
vec.replace(i, temp.removeMax()) ;
}
public static void main(String args[]){
Random rnd = new Random() ;
FixedVector fvec = new FixedVector() ;
fvec.append(rnd.nextInt(10)) ;
fvec.append(rnd.nextInt(10)) ;
fvec.append(rnd.nextInt(10)) ;
fvec.append(rnd.nextInt(10)) ;
fvec.append(rnd.nextInt(10)) ;
fvec.append(rnd.nextInt(10)) ;
fvec.append(rnd.nextInt(10)) ;
fvec.append(rnd.nextInt(10)) ;
fvec.append(rnd.nextInt(10)) ;
fvec.append(rnd.nextInt(10)) ;
heapSort(fvec) ;
for(int i=0; i<fvec.size(); i++)
System.out.print(fvec.elementAt(i) + "\t") ;
}
}
复杂度分析
average case for Heap Sort in O(n*lg(n))
5 归并排序(Merge Sort)
算法描述
- 归并排序时采用递归的方法进行排序,递归的策略是“分而治之”
- 直到分解为最小单位为包含一接口一个元素的序列,再进行合并
- 合并的时候将序列抽离出来为新的序列,同时多加一个哨兵元素,再依次比较两个序列元素的大小,然后替换掉原来的元素进行排序
算法动画演示
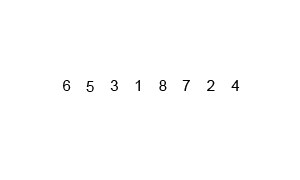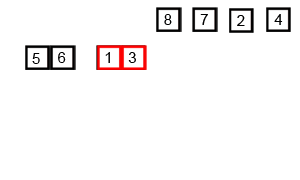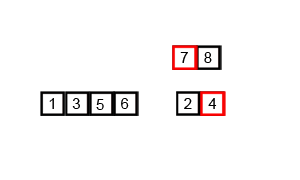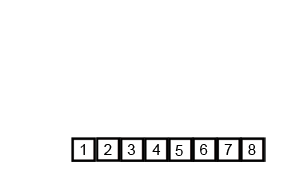
算法实现
import java.util.Random ;
public class MergeSort{
static void mergeSort(int[] array, int lo, int hi){
if(lo+1 == hi)
return ;
int mid = (lo + hi)/ 2 ;
mergeSort(array, lo, mid) ;
mergeSort(array, mid, hi) ;
merge(array, lo, mid, hi) ;
}
static void merge(int[] array, int lo, int mid, int hi){
int[] array_lt = new int[mid - lo + 1] ;
int[] array_rt = new int[hi - mid + 1] ;
for(int i = 0; i < array_lt.length-1; i ++)
array_lt[i] = array[lo + i] ;
for(int i = 0; i < array_rt.length-1; i ++)
array_rt[i] = array[mid + i] ;
array_lt[array_lt.length-1] = Integer.MAX_VALUE ; // 增加一个哨兵元素
array_rt[array_rt.length-1] = Integer.MAX_VALUE ; // 增加一个哨兵元素
int i = 0 ;
int j = 0 ;
for(int k = lo; k < hi; k ++){
if(array_lt[i] < array_rt[j]){
array[k] = array_lt[i] ;
i ++ ;
}else{
array[k] = array_rt[j] ;
j ++ ;
}
}
}
public static void main(String args[]){
Random rnd = new Random() ;
int[] array = new int[10] ;
for(int i = 0; i < array.length; i ++)
array[i] = rnd.nextInt(10) ;
mergeSort(array, 0, array.length) ;
for(int i : array)
System.out.print(i + "\t") ;
}
}
复杂度分析
average case for Merge Sort in O(n*lg(n))
6 快速排序(Quick Sort)
算法描述
- 快速排序和归并和排序相似,是采用分而治之的策略递归进行的
- 将序列分解成两个相互关联的子序列,在中间找出一个所谓的”pivot”的数
- 将两个子序列转变成:左边子序列中的每一个元素都小于或者等于”pivot”;右边子序列中的每一个元素都大于或者等于”pivot”。通过方法”medianOf3,partition”完成
- 递归调用”medianOf3,partition”方法,完成排序
算法动画演示
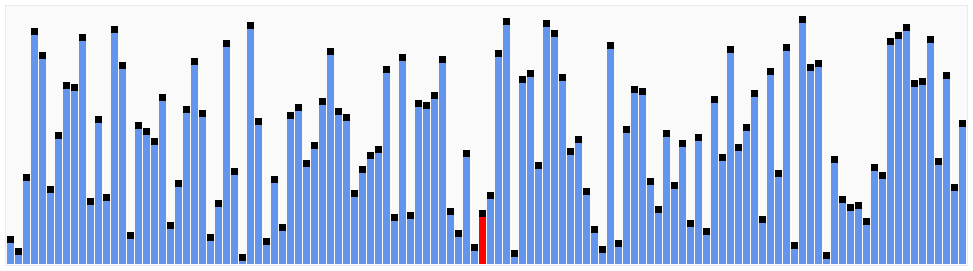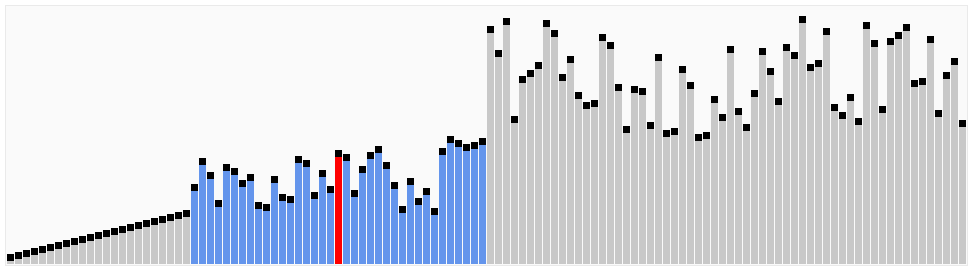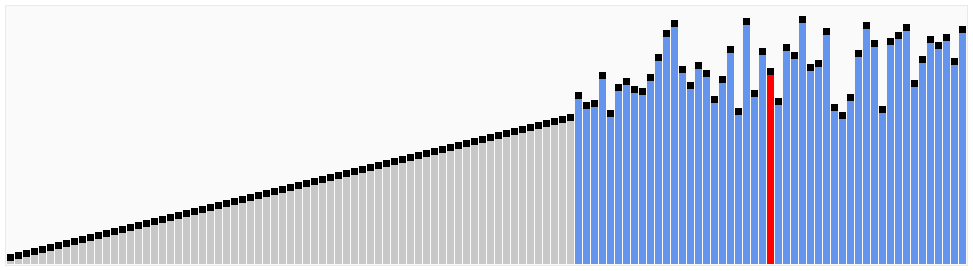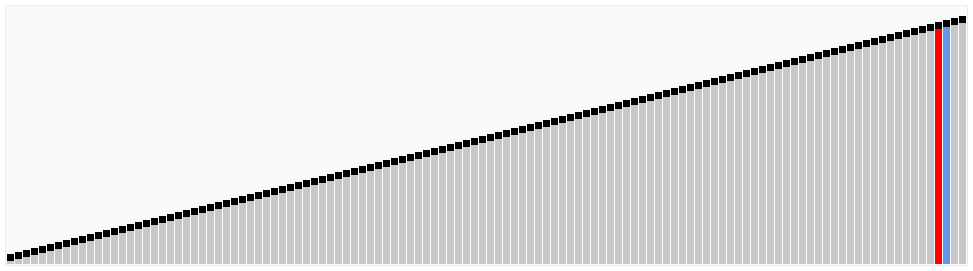
算法实现
import java.util.Random ;
public class QuickSort{
protected static void swap(int[] array, int first, int last){
int temp = array[first] ;
array[first] = array[last] ;
array[last] = temp ;
}
protected static void medianOf3(int[] array, int lo, int hi){
int mid = (lo + hi) >> 1 ;
if(array[lo] > array[mid])
swap(array, lo, mid) ;
if(array[mid] > array[hi-1])
swap(array, mid, hi-1) ;
if(array[lo] > array[mid])
swap(array, lo, mid) ;
}
protected static int partition(int[] array, int lo, int hi){
int mid = (lo + hi) / 2 ;
int pivot = array[mid] ;
while(true){
while(array[++ lo] < pivot) ;
while(array[-- hi - 1] > pivot) ;
if(lo > hi - 1)
break ;
else
swap(array, lo, hi - 1) ;
}
return lo ;
}
static void quickSort(int[] array, int lo, int hi){
if(lo - hi <= 10)
InsertionSort.insertionSort_v2(array, lo, hi) ;
else{
medianOf3(array, lo, hi) ;
int left_prt = partition(array, lo, hi) ;
quickSort(array, lo, left_prt) ;
quickSort(array, left_prt + 1, hi - 1) ;
}
}
public static void main(String args[]){
Random rnd = new Random() ;
int[] array = new int[50] ;
for(int i = 0; i < array.length; i ++)
array[i] = rnd.nextInt(10) ;
quickSort(array, 0, array.length) ;
for(int i : array)
System.out.print(i + ",") ;
}
}
复杂度分析
average case for Quick Sort is in O(n*lg(n))
7 Shell排序(Shell Sort)
算法描述
- Shell排序算法是以它的发明者D.L.Shell命名的
- Shell算法是Insertion Sort算法的推广
- 算法的关键是使用了”h-increment”,也就是相当于在间隔h的元素上进行Insertion Sort
- h的值不断变小,最后变成了1,也就是完全意义上的Insertion Sort
算法动画演示
算法实现
import java.util.Random ;
public class ShellSort{
static void shellSort(int[] array, int lo, int hi){
int current ;
int pos ;
int insert_value ;
int h = 1 ;
while(h < hi)
h = h * 3 + 1 ;
while(h > 0){
for(current = h; current < hi && current >= lo; current ++){
insert_value = array[current] ;
pos = current ;
while(pos > h - 1 && insert_value < array[pos - h]){
array[pos] = array[pos - h] ;
pos -= h ;
}
array[pos] = insert_value ;
}
h = (h - 1) / 3 ;
}
}
public static void main(String args[]){
Random rnd = new Random() ;
int[] array = new int[20] ;
for(int i = 0; i < array.length; i ++)
array[i] = rnd.nextInt(10) ;
shellSort(array, 0, array.length) ;
for(int i : array)
System.out.print(i + ",") ;
}
}
复杂度分析
利用sequence[1, 2, 8, 2^(k-1),.],the Shell Sort is in O(n^1.5)
