目录
- 0 前言
- 1 Vector(array-based)
- 2 Heap(array-based)
- 3 抽象化Vector、Heap
- 4 Stack(sequential-based, single link)
- 5 Queue(sequential-based, double link)
- 6 Deque(Sequential-based, double link)
- 7 抽象化Stack、Queue、Deque
- 8 抽象化ArrayContainer、LinearLikedContainer
- 9 完全抽象化(ArrayContainer、LinearLikedContainerinear、TreeContainer
- 10 GeneralBinaryTree(sequential-based,tree link)
- 11 BinarySearchTree(sequential-based,tree link)
0 前言
跟着我,一步一个脚印,学习数据结构与算法
从底层实现是数组的Vector、Heap到底层实现是链表的Stack、Queue、Deque、BinaryTree、BinarySearchTree,一步一步用源代码解开数据结构神秘的面纱
目的
- 消除对数据结构和算法的恐惧,其实也就那么回事
- 从一个DSA的小白到在自己脑海中构建可视化的数据结构
- 理解数据结构的底层是怎么实现的,能够私人订制自己的数据结构
- 在工作中遇到问题,知道从什么样的数据就够入手去解决问题
- 对OOP(面向对象编程)思想有更加深刻的理解
注意
- 只针对DSA的小白,如果你是大神,请指教
- 可视化的重要性,要在脑海中建立抽象模型
- 源代码要看完之后自己coding
- Git项目step_by_step_learn_DSA的
src目录下有源代码和大量的测试代码,所有代码均为亲测可行
亮点
- 使用UML(统一建模语言)进行代码的自动生成
- UML类图能够可视化类之间的关系,帮助理解结构之间的关系
- 有详细的源代码和测试代码
- 代码有详细的演变和泛化过程,帮助理解面向对象的抽象化
工具
- Enterprise Architect,工业界使用广泛的UML建模工具
- Java,数据结构用Java语言实现
如果想获得Enterprise Architect(version12.1)工业版免费安装,请留言邮箱。
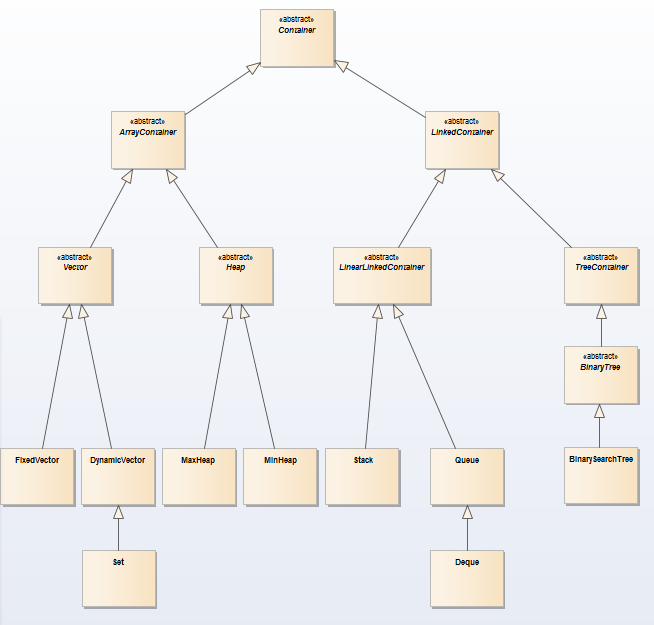
结构框架
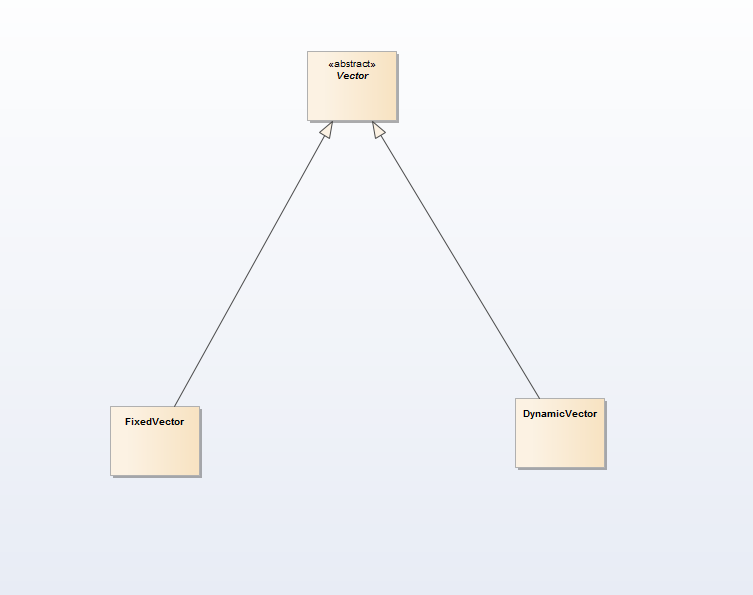
1 Vector(array-based)
vector: a random-access collection of elements
操作:
- append(element) : 添加一个新的元素到这个Collection中
- clear() : 清空这个Collection
- contains(element) : Collection中是否含有元素element
- elementAt(index) : 获取相应index的元素
- indexOf(element) : 获取element的index
- insertAt(index, element) : 在指定的index处插入element
- isEmpty() : Collection是否为空
- removeAt(index) : 删除指定index的element
- remove(element) : 删除Collection中指定的element
- replace(index, element) : 替换掉指定index处的元素为element
- size() : Collection共包含多少个元素
FixedVector: 是传统意义上的Vector,也就是数组的一个简单包装。当Collection的容量等于Collection的size()的时候,就不能执行append()和insertAt()操作。
DynamicVector: 是一个动态的Vector,当Collection的容量等于Collection的size()的时候,要记性插入操作就要动态的扩充Collection的容量。
Implementation
2 Heap(array-based)
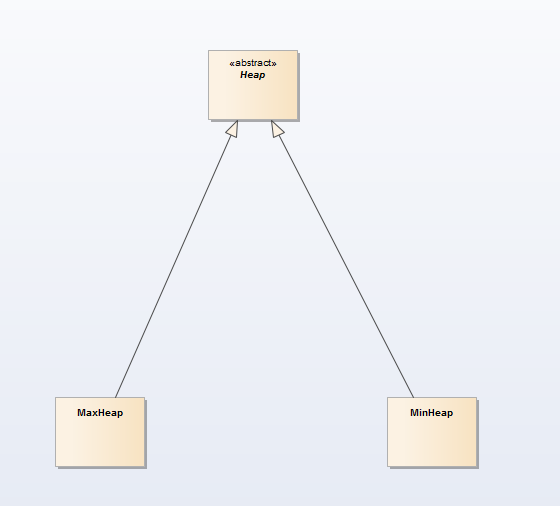
Heap : Heap是一个“部分有序完全二叉树(partially ordered complete binary tree)”;部分有序指:堆的父元素总是比子元素小(大),父元素比子元素大称之为MaxHeap,父元素比子元素小称之为MinHeap。
二叉树元素n的深度:从root开始到元素n必须经由的边的个数
二叉树的高度:最深的一个元素的深度加1
同样深度的元素为同一个level
完全二叉树:二叉树的填充顺序是从root开始,从左到右依次填充每一个level
操作:
- clear() : 清空Collection
- insert(element): 插入一个新的元素到Collection
- isEmpty() : Colloection是否为空
- peek() : 得到root元素
- remove() : 删除root元素
- size() : Collection中有多少个元素
Implementation
Heap应用
- 堆排序(MinHeap)
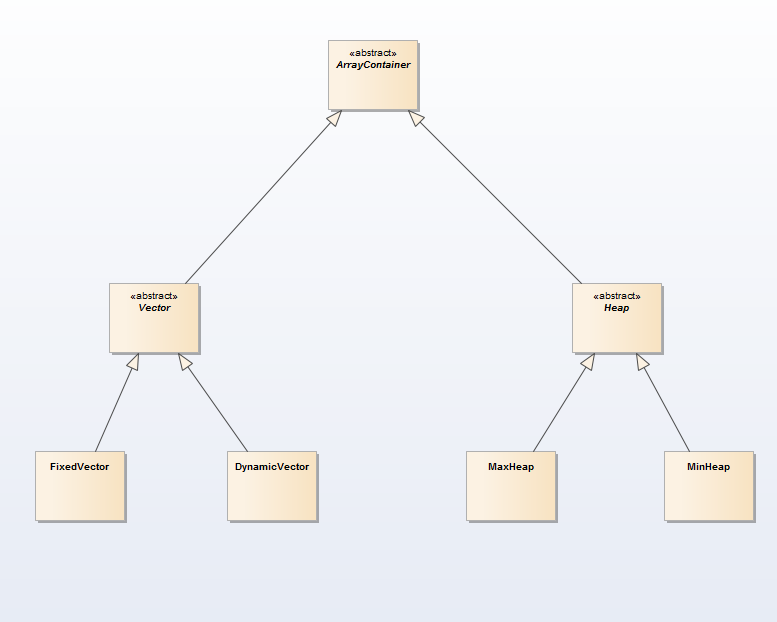
3 抽象Vector和Heap为ArrayContainer
Vector和Heap都是array-based,因此我们可以将二者抽象为ArrayContainer
ArrayContainer
4 Stack(sequential-based, single lined-list)

我们可以很容易的使用array container来实现Stack,但是我们通常使用链表来实现Stack。
使用链表实现Stack的原因
- Stack不是random-access的
- 使用数组实现的栈并不能使用上random-access的功能
- 使用数组实现的栈浪费空间,因为Collection的容量总是大于Collection的size()
链表(linked list)
链表是一组nodes的线性组合,组合中的每一个node至少提供a data和a link portion;一个node的link portion是一个指针或者引用执行组合中的下一个node。
Stack: 一组线性元素组成的Collection,只能够从Collection的一端获取元素。我们所感兴趣的当前元素称之为top元素
操作:
- clear() : 清空Collection
- isEmpty() : 判断Collection是否为空
- pop() : 删除top元素
- push(element) : 把指定的element推入栈,最为topelement
- size() : Collection共有多少个元素
- top() : 得到top元素
linear liked node
Implementation
Stack应用
- 括号匹配
- 中缀表达式计算
中缀表达式的软代码中使用的是java自带的Stack数据结构
5 Queue(sequential-based, double linked-list)

Queue: 一组线性元素组成的Collection,只能从Collection的末尾获取元素;我们感兴趣的元素称之为front element;最后一个元素称之为back element
操作:
- clear() : 清空Collection中的元素
- front() : 得到Collection的front element
- insertBack() : 向Collection的队尾添加元素,称为back element
- isEmpty() : 判断Collection是否为空
- removeFront() : 删除front element
- size() : Collection中共有多少个元素
我们用单链表实现了Stack数据结构,由于队列有对头和对尾,我们要使用双链表实现Queue数据结构
修改上述的LineaNode为SLNode(Single linear linked node)
Double linear linked node
Implementation
Queue应用
- 打印机
- 计算机仿真
6 Deque(sequential-based, double linked-list)
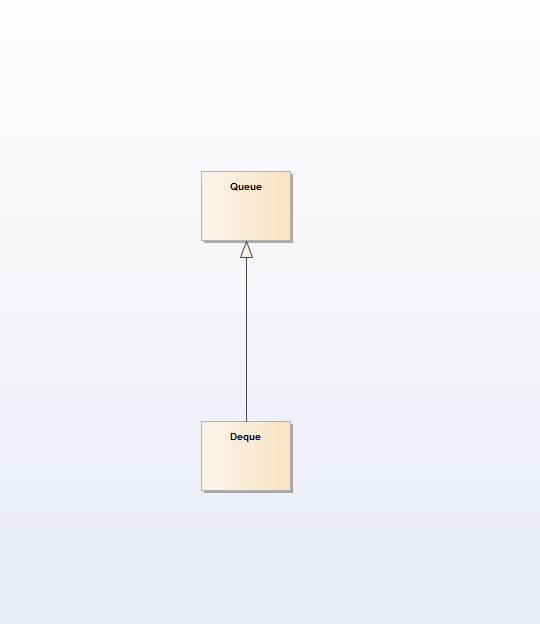
Deque: 称之为double-ended queue;可以在队列两段进行插入和删除操作
Deque继承Queue,比Queue增加的功能为可以任意的一端进行插入和删除操作
操作:
- back() : 得到Collection的back element
- clear() : 清空Collection
- front() : 得到Collection的front element
- insertBack() : 插入元素为back element
- insertFront() : 插入元素为front element
- removeBack() : 删除back element
- removeFront() : 删除front element
- size() : Collection含有多少个元素
Implementation
Deque应用
- web browser’s history
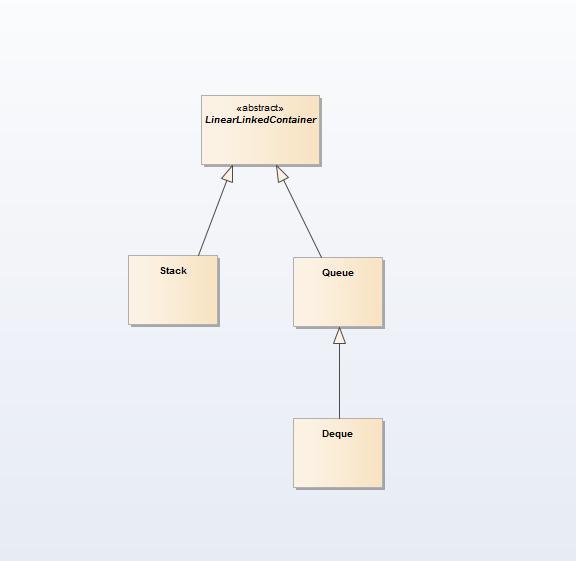
7 抽象化Stack、Queue和Deque为LinearLinkedContainer
8 抽象化LinkedContainer和ArrayContainer为Container
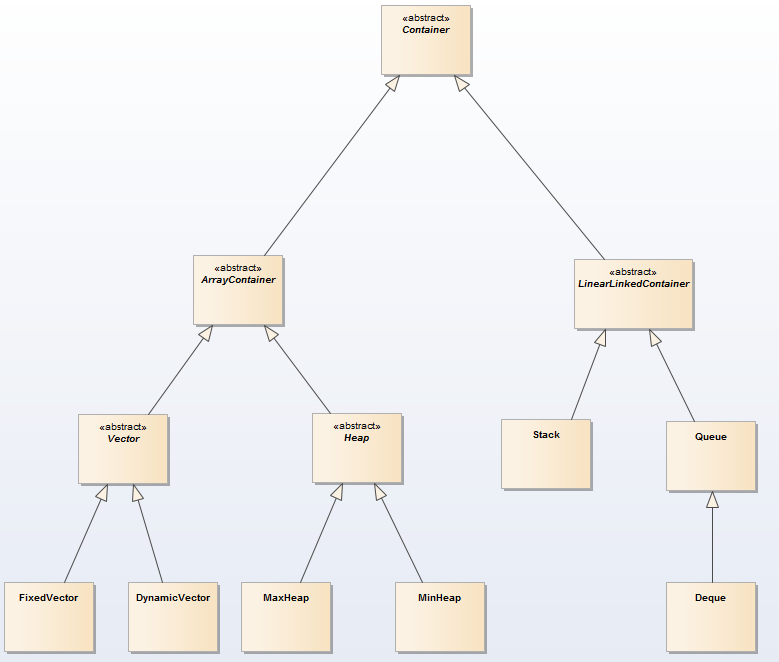
9 进一步抽象化Container
接下来我们要讲解General Binary Tree,由于General Binary Tree是Linked Container,但是不是Linear Linked Container,所以我么有必要将我们的UML模型记性进一步的抽象。

Container-ArrayContiner部分
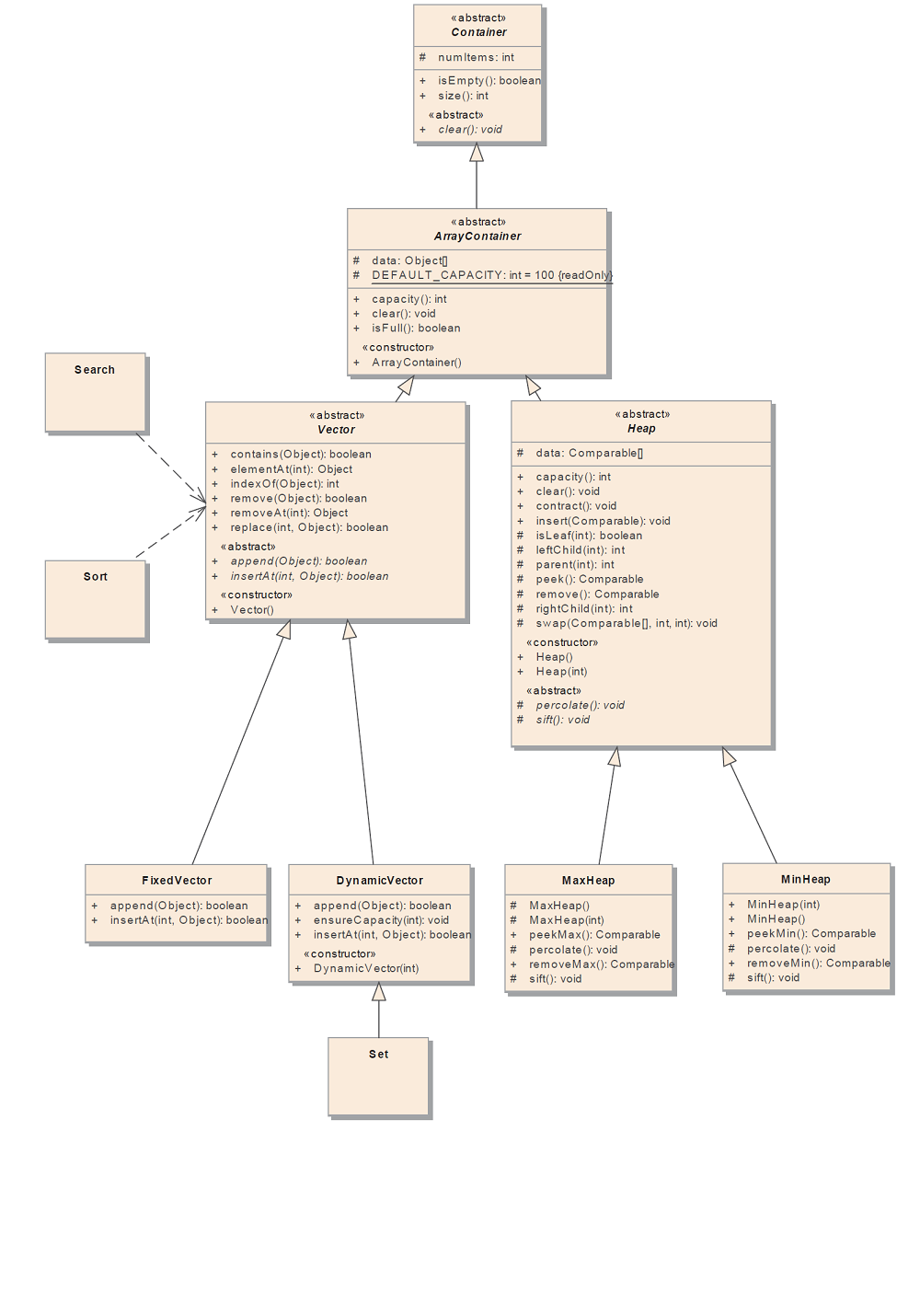
源代码
Container-LinkedContainer部分
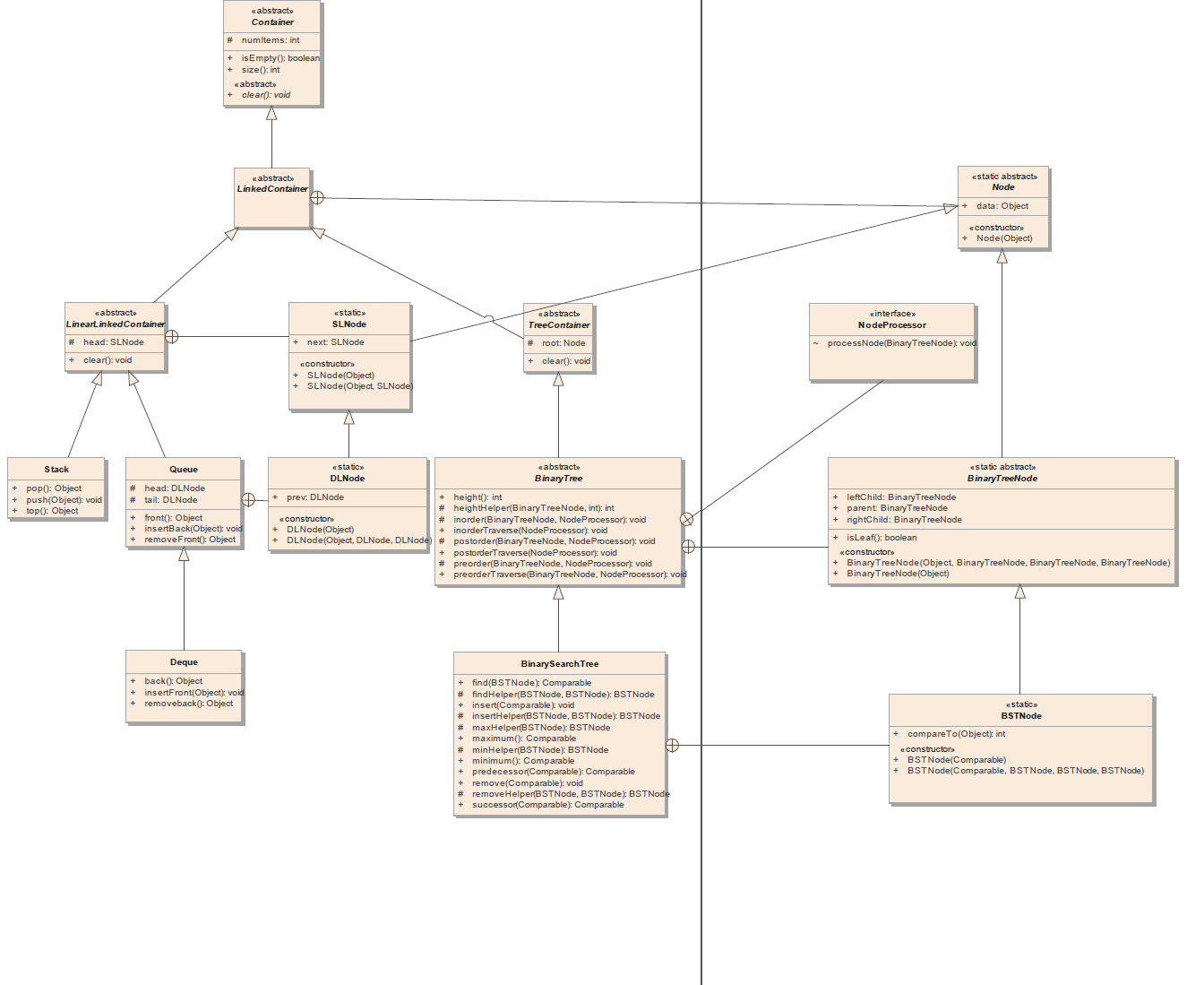
源代码
10 General Binary Tree

操作:
- clear() : 清空Collection
- height() : 二叉树的高度
- inorderTraverse() : 中序遍历
- postorderTraverse() : 后序遍历
- preorderTraverse() : 前序遍历
- size() : Collection中包含的元素的多少
Implementation
此时我们已经建立的完全的抽象模型,实现也是基于模型进行。
BinaryTree的应用
- Huffman coding
- Expression Tree
11 BinarySearchTree(BST)
BST: 是一个绝对有序的二叉树(totally ordered binary tree)。绝对有序指的是:一个node的leftChild的data小于node的data;node的rightChild的data大于或者等于node的data。
操作:
- clear() : 清除Collection
- find(element) : 查找指定的element
- inorderTraverse(processor) : 中序遍历
- insert(element) : 插入element到Collection中
- isEmpty() : 判断Collection是否为空
- maximum() : 得到Collection的最大element
- minimum() : 得到Collection的最小element
- postorderTraverse(processor) : 后序遍历
- predecessor(element) : get the inorder predecessor of the given element
- preorderTraverse(processor) : 前序遍历
- remove(element) : 从Collection中删除指定的element
- successor() : get the inorder successor of the given element
Implementation
BST应用
- dictionary
