目录
问题描述
数据库中的数据如下图:
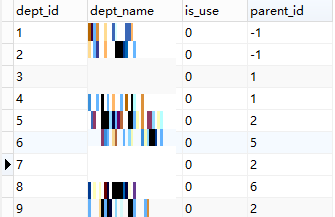
建表语句:
-- mysql建表语句
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS "sys_dept";
CREATE TABLE "sys_dept" (
"dept_id" varchar(300) DEFAULT NULL,
"dept_name" varchar(300) DEFAULT NULL,
"is_use" varchar(300) DEFAULT NULL,
"parent_id" varchar(300) DEFAULT NULL
)
INSERT INTO "sys_dept" VALUES ('1', '01', '0', '-1');
INSERT INTO "sys_dept" VALUES ('2', '12', '0', '-1');
INSERT INTO "sys_dept" VALUES ('3', '123', '0', '1');
INSERT INTO "sys_dept" VALUES ('4', '1234', '0', '1');
INSERT INTO "sys_dept" VALUES ('5', '12345', '0', '2');
INSERT INTO "sys_dept" VALUES ('6', '123456', '0', '5');
INSERT INTO "sys_dept" VALUES ('7', '1234567', '0', '2');
INSERT INTO "sys_dept" VALUES ('8', '12345678', '0', '6');
INSERT INTO "sys_dept" VALUES ('9', '123456789', '0', '2');
需要将上述数据转化为JSON,格式为:
[{
"id": "1",
"name": "01",
"childrenList": [{
"id": "3",
"name": "123"
},
{
"id": "4",
"name": "1234"
}]
},
{
"id": "2",
"name": "**12",
"childrenList": [{
"id": "5",
"name": "12345",
"childrenList": [{
"id": "6",
"name": "123456",
"childrenList": [{
"id": "8",
"name": "12345678"
}]
}]
},
{
"id": "7",
"name": "1234567"
},
{
"id": "9",
"name": "123456789"
}]
}]
Mybatis collection一对多递归调用方法
数据对应的POJO对象为:
public class DeptTree {
private String id;
private String name;
private List<DeptTree> childrenList;//子节点
...
}
Mapper文件:
<select id="selectDeptChildrenById" resultMap="deptTree" parameterType="string">
select dept_id, dept_name from sys_dept
-->
<!-- 当有参数注入的时候,不能写为1行:
select dept_id, dept_name from "public"."sys_dept" where parent_id = #{id}
-->
where parent_id = #{id}
</select>
<!-- Mybatis resultMap collection标签下面有select属性,可以递归调用 -->
<!-- 这种递归调用的方式存在性能问题慎重使用 -->
<resultMap type="com.fmz.learn.spring.pojo.DeptTree" id="deptTree">
<id column="dept_id" property="id" javaType="java.lang.String"/>
<result column="dept_name" property="name" javaType="java.lang.String"/>
<collection property="childrenList" column="dept_id" ofType="com.fmz.learn.spring.pojo.DeptTree"
javaType="java.util.ArrayList"
select="com.fmz.learn.spring.mapper.GetDeptTree.selectDeptChildrenById"/>
</resultMap>
使用方法:mapper.selectDeptChildrenById("-1")调用时,会在resultMap中发生递归调用,生成JSON对应的实体类。
这种递归调用的方法,会一遍一遍的执行子查询,有性能方面的问题。
程序中递归调用方法
考虑到上面方法执行的性能问题,事实上,当数据有5000条左右时,执行的时间就需要15s左右。
想通过在程序中递归调用的方法执行。
service层的递归方法:
private void getDeptTree(List<DeptTree> result){
for(DeptTree dt : result) {
List<DeptTree> childrenList = getDeptTree.selectDeptChildrenById(dt.getId());
if(childrenList != null){
dt.setChildrenList(childrenList);
}
getDeptTree(dt.getChildrenList());//这里是递归调用
}
}
Mapper文件:
<resultMap type="com.fmz.learn.spring.pojo.DeptTree" id="deptTree">
<id column="dept_id" property="id" javaType="java.lang.String"/>
<result column="dept_name" property="name" javaType="java.lang.String"/>
</resultMap>
result是传进来的根节点的数据,递归根节点的数据,配合查询数据库来将设置子节点。
事实上,这种方法比第一种方法还要糟糕,原因除了每次递归调用要执行SQL之外,还要有访问数据库的消耗。
这种在递归调用中访问数据库的方式在开发公司的技术规范中都是命令禁止的。
基础数据加载到内存后递归调用方法
**使用mybatis
再考虑,需要将每个节点及其子节点的数据都先出来,在递归中使用到的时候不去数据库查询,而直接从内存中读取,这样就不存在性能的问题了。
Mapper文件:
<select id="queryParentidChildrenMap" resultMap="deptTreeMap">
select * from sys_dept
</select>
<resultMap type="com.fmz.learn.spring.pojo.DeptTree" id="deptTreeMap">
<id column="parent_id" property="id" javaType="java.lang.String"/>
<collection property="childrenList" ofType="com.fmz.learn.spring.pojo.DeptTree">
<id property="id" column="dept_id" javaType="java.lang.String" />
<id property="name" column="dept_name" javaType="java.lang.String" />
</collection>
</resultMap>
需要将Mapper映射得到的数据转化为一个Map,这样方便递归时查询:
private Map<String, List<DeptTree>> compactMap(List<DeptTree> paramResult) {
Map<String, List<DeptTree>> result = new HashMap<>();
for(DeptTree dt : paramResult) {
result.put(dt.getId(), dt.getChildrenList());
}
return result;
}
使用上述得到的Map,再递归设置子节点:
private void getDeptTree(List<DeptTree> result, Map<String, List<DeptTree>> map) {
for(DeptTree dt : result) {
List<DeptTree> childrenList = map.get(dt.getId());
if(childrenList != null){
dt.setChildrenList(childrenList);
getDeptTree(dt.getChildrenList(), map);
}
}
}
**不使用mybatis
基本映射pojo类:
package com.thunisoft.artery.service.ywdm.bean;
public class Ywdm {
private Integer pid;
private Integer dm;
private String mc;
private Integer kwh;
private String fjxx;
private Integer yx;
private Integer xssx;
private String dmjp;
private String jb;
//omit setter and getter
}
树节点pojo类:
public class JqSTNode {
/** 节点的id,唯一 */
private String id;
/** 节点的类型 */
private String type;
/** 节点的显示名称 */
private String name;
/** 是否为父节点 */
private Boolean isParent = false;
/** 是否直接展开此节点,仅非异步加载时生效 */
private Boolean open = false;
/** checkbox/radio是否勾选 */
private Boolean checked = false;
/** checkbox/radio是否隐藏 */
private Boolean nocheck = false;
/** checkbox/radio是否禁用 */
private Boolean chkDisabled = false;
/** 图标的URL路径 */
private String icon;
/** 父节点折叠时图标的URL路径 */
private String iconClose;
/** 父节点展开时图标的URL路径 */
private String iconOpen;
/** 图标的className */
private String iconSkin;
/** 子节点 */
private List<JqSTNode> children;
/** 父节点:后台使用,不输出到前台json数据中 */
private JqSTNode parent;
/** 用户自定义参数,输出到前台 */
private Map<String, Object> custParams;
private String title;
public void setChildren(List<JqSTNode> children) {
this.children = children;
if (null != this.children && !this.children.isEmpty()) {
for (JqSTNode jqSTNode : children) {
jqSTNode.setParent(this);
}
}
}
public Map<String, Object> getCustParams() {
if (custParams == null) {
custParams = new HashMap<String, Object>();
}
return custParams;
}
// omit unnecessary setting and getter
}
mybatis基本查询映射:
<!-- 通用查询映射结果 -->
<resultMap id="BaseResultMap" type="com.thunisoft.artery.service.ywdm.bean.Ywdm">
<id column="n_dm" property="dm" />
<result column="n_bh_dmlx" property="pid" />
<result column="c_mc" property="mc" />
<result column="n_kwh" property="kwh" />
<result column="c_fjxx" property="fjxx" />
<result column="n_yx" property="yx" />
<result column="n_xssx" property="xssx" />
<result column="c_dmjp" property="dmjp" />
<result column="c_jb" property="jb" />
</resultMap>
<sql id="base_column_sql">
n_bh_dmlx,n_dm,c_mc,n_kwh,c_fjxx,n_yx,n_xssx,c_dmjp,c_jb
</sql>
<select id="selectByPid" resultMap="BaseResultMap">
select
<include refid="base_column_sql"></include>
from schema.table
where n_bh_dmlx = #{pid}
order by n_xssx
</select>
业务代码构建树:
public class YwdmService {
@Resource
private YwdmMapper ywdmMapper;
public List<Ywdm> selectByPid(Integer pid){
return ywdmMapper.selectByPid(pid);
}
//基础映射pojo到树节点pojo赋值
public List<JqSTNode> loadTree(Integer pid) {
List<JqSTNode> allNodes = Lists.newArrayList();
List<Ywdm> ywdms = ywdmMapper.selectByPid(pid);
ywdms.forEach(dm ->{
JqSTNode node = new JqSTNode();
node.setId(String.valueOf(dm.getDm()));
node.setName(dm.getMc());
node.setIsParent(StringUtils.isBlank(dm.getFjxx()));
Map<String, Object> params = Maps.newHashMap();
params.put("fid", dm.getFjxx());
node.setCustParams(params);
allNodes.add(node);
});
return recursiveGetList(allNodes);
}
//递归设置children
private List<JqSTNode> getChildNode(JqSTNode dm, List<JqSTNode> allNodes) {
List<JqSTNode> childNodeList = allNodes.stream().filter(node -> StringUtils.equals(String.valueOf(node.getCustParams().get("fid")), dm.getId())).map(
entity ->{
entity.setChildren(getChildNode(entity, allNodes));
return entity;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
return childNodeList;
}
//构建树
public List<JqSTNode> recursiveGetList(List<JqSTNode> allNodes) {
List<JqSTNode> collect = allNodes.stream().filter(node -> node.getIsParent()).map(dm -> {
dm.setChildren(getChildNode(dm, allNodes));
if(CollectionUtils.isEmpty(dm.getChildren())){
dm.setIsParent(false);
}
return dm;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
return collect;
}
}
